National Blood Donor Month
Welcome to National Blood Donor Month, a time dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of donating blood and saving lives. Each year, countless individuals rely on the selfless act of donors to receive life-saving transfusions. Whether you’re a first-time donor or a regular supporter, your contribution can make an incredible difference in someone’s life. So, let’s dive into the vital reasons why donating blood is so crucial for patients in need. Give blood, donate blood, and join us in this noble mission to save lives!
Why is it Important to Donate Blood?
Why is it Important to Donate Blood?
Donating blood is a simple yet powerful act of kindness that can have a profound impact on the lives of others. When you donate blood, you are giving someone a lifeline, a chance at survival. Your donation can help patients undergoing surgeries, cancer treatments, and other medical procedures.
One of the key reasons why donating blood is important is because there is simply no substitute for human blood. Despite advances in medical technology, synthetic alternatives cannot replicate the intricate composition and life-sustaining properties of real blood.
Moreover, donated blood plays a crucial role in emergency situations where time is of the essence. Accidents, natural disasters, and unforeseen medical emergencies often require immediate transfusions to save lives. By donating regularly, you ensure that there’s an adequate supply readily available when these urgent situations arise.
Additionally, some individuals suffer from chronic conditions or diseases that necessitate regular transfusions to manage their health effectively. Conditions such as sickle cell anemia or certain types of cancer rely heavily on donated blood to provide relief and improve quality of life for these patients.
By donating your own blood, you become part of a community effort to support those who depend on these life-saving transfusions every day. It’s not just about one person making a difference; it’s about all donors collectively coming together to create an impact greater than themselves.
So if you’re wondering how you can make a positive change in someone’s life today—look no further than donating blood. The benefits extend far beyond yourself; they reach out to touch the lives of countless individuals who desperately need your help.
ALL PATIENTS MUST HAVE A HEALTH ASSESSMENT PRIOR TO DONATING BLOOD
Before donating blood, it is crucial for all patients to undergo a thorough health assessment. This step ensures the safety of both donors and recipients during the transfusion process.
During the health assessment, a phlebotomist will draw a blood sample to conduct various tests. These tests include checking for blood type, Rh factor, infectious diseases, and conditions like sickle cell disease.
One of the primary reasons for this assessment is to determine the compatibility of blood types between donors and recipients. Matching blood types correctly can mean the difference between life and death for someone in need of a transfusion.
Additionally, testing for infectious diseases in donated blood is essential to prevent transmission through transfusions. Common transmissible diseases that are screened for include HIV, hepatitis viruses, Parvo B19 virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), West Nile virus, and human T-Cell lymphotropic viruses.
By conducting these assessments prior to donation, healthcare professionals ensure that only safe and compatible blood is given to those who require it most.
Remember: giving blood saves lives! So if you meet the necessary health requirements and are able to donate safely – consider becoming a donor today!
After drawing a blood sample which is done by a phlebotomist the blood is then checked for Blood type, Rh factor, infectious disease and Sickle cell.
After a blood sample is drawn by a skilled phlebotomist, it undergoes a series of crucial tests to ensure its safety and compatibility for transfusion. The first step in this process involves determining the blood type and Rh factor. These factors play a vital role in matching donated blood with recipients who require transfusions.
Additionally, the sample is screened for infectious diseases that can be transmitted through transfusions. This includes testing for viruses such as HIV, Hepatitis, Parvo B 19, Cytomegalovirus, West Nile Virus, and Human T-Cell Lymphotropic viruses. By identifying these potential risks beforehand, healthcare professionals can safeguard against any harm to patients who may receive the donated blood.
Another important test conducted on the blood sample is screening for Sickle cell disease. This inherited condition affects red blood cells’ ability to carry oxygen effectively throughout the body. Identifying individuals with Sickle cell disease ensures they receive appropriate treatment and prevents complications during transfusions.
By thoroughly assessing various aspects of donated blood samples like Blood type, Rh factor, infectious diseases screenings, and Sickle cell detection helps guarantee safe and effective transfusions that save lives every day.
Testing for Infectious Disease in the blood which can be transmitted during a blood transfusion.
Testing for infectious diseases in the blood is a crucial step to ensure the safety of blood transfusions. This screening process helps identify any potential viruses or infections that can be transmitted through donated blood.
Various infectious diseases are tested, including Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis virus, Parvo B19 virus, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), West Nile virus, and Human T-Cell Lymphotropic viruses. By testing for these infections, healthcare professionals can prevent the transmission of harmful diseases to patients receiving blood transfusions.
The detection of these infectious agents involves conducting thorough laboratory tests on donated blood samples. The goal is to identify any presence of these pathogens accurately. This meticulous screening process ensures that only safe and disease-free blood is used for transfusion purposes.
By implementing rigorous testing protocols, the risk of transmitting infectious diseases through blood transfusions is significantly reduced. It provides peace of mind not just for patients who require life-saving transfusions but also for their families and medical professionals involved in their care.
Testing for infectious disease in donated blood plays a vital role in ensuring patient safety during transfusions. These screenings help prevent the transmission of harmful viruses and infections from donors to recipients. By adhering to strict testing protocols, we can continue to provide safe and effective treatments while saving lives through the gift of donated blood.
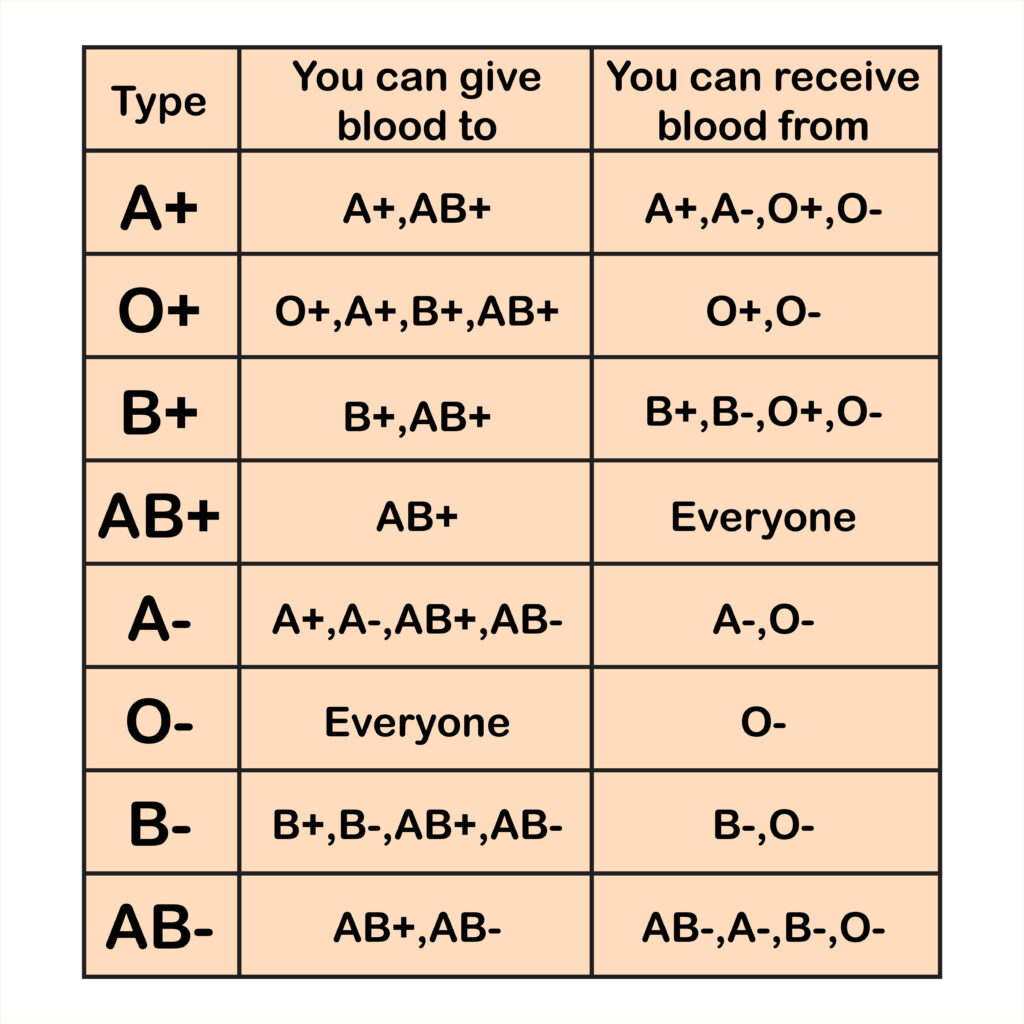
Blood types and why they are important
Blood types play a crucial role in ensuring safe and successful blood transfusions. There are four main blood types – A, B, AB, and O – which are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Additionally, each blood type can be positive (+) or negative (-), based on the presence or absence of another antigen called Rh factor.
Matching blood types is essential because if incompatible blood is transfused into a patient, it can lead to serious complications and even death. For example, if someone with Type A receives Type B blood, their immune system will recognize the foreign antigens as threats and mount an attack against them.
The universal red cell donor is someone with Type O negative (O-), meaning they do not have A or B antigens on their red cells nor does their plasma contain antibodies against these antigens. This makes O- compatible with all other blood types. On the other hand, individuals with Type AB positive (AB+) are considered universal plasma donors since they can donate plasma to any recipient regardless of their own blood type.
Understanding your own blood type is important not just for potential donations but also for medical purposes such as surgeries or emergencies where quick access to matched units may be required. It’s always helpful to know your own type and encourage others to do so too!
By donating blood that matches certain criteria such as Rh factor and infectious disease screening results you’re giving patients in need a chance at life-saving treatment! So consider being a part of National Blood Donor Month by giving back through donation today!
There are very specific ways in which blood types must be matched for a safe transfusion.
“The right blood transfusion can mean the difference between life and death. Use the interactive graphic below to learn more about matching blood types for transfusions. Also, Rh-negative blood is given to Rh-negative patients, and Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood may be given to Rh-positive patients. The rules for plasma are the reverse. • The universal red cell donor has Type O negative blood. • The universal plasma donor has Type AB blood” https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-types.html
Matching blood types for transfusions is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful procedure. The right blood transfusion can make all the difference between life and death. That’s why there are specific protocols in place to ensure compatibility.
When it comes to blood types, there are several factors to consider. Rh-negative blood is typically given to Rh-negative patients, while Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood may be given to Rh-positive patients. These guidelines help prevent adverse reactions during transfusions.
In terms of red cell donations, Type O negative is considered the universal donor. This means that individuals with this blood type can donate their red cells to patients of any other blood type without causing an immune response.
On the other hand, when it comes to plasma donations, Type AB blood is considered the universal donor. This means that individuals with Type AB blood can donate their plasma to patients of any other ABO group.
Understanding these rules and guidelines for matching blood types is essential in promoting successful transfusions and ultimately saving lives. So if you’re considering donating blood, knowing your own type can provide valuable information on how you can contribute effectively!
Testing for Infectious Disease in the blood which can be transmitted during a blood transfusion.
Testing for Infectious Disease in the blood is a crucial step in ensuring the safety of blood transfusions. Transmissible diseases can have serious consequences if they are unknowingly transferred through donated blood. That’s why thorough screening is conducted to detect common transmissible diseases such as HIV, Hepatitis Virus, Parvo B 19 Virus, Cytomegalovirus, West Nile Virus, and Human T-Cell Lymphotropic viruses.
The testing process involves checking each blood sample for the presence of these infectious agents. By identifying any potential risks before a transfusion takes place, healthcare professionals can prevent the transmission of these diseases and safeguard the health of patients who rely on donated blood.
It’s important to stay updated on the latest information regarding transmissible diseases and their detection methods. Medical professionals like Mudassar Zia, MD and Emmanuel C Besa, MD work tirelessly to ensure that accurate knowledge is available for effective screening protocols.
The most common transmissible disease are the following: Human immunodeficiency virus or (HIV) Hepatitis Virus Parvo B 19 Virus Cytomegalovirus West Nile Virus Human T-Cell Lymphotropic viruses (Updated: Apr 08, 2021 • Author: Mudassar Zia, MD; Chief Editor: Emmanuel C Besa, MD https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1389957-overview)
Through ongoing research and advancements in medical technology, we can continue improving our ability to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with transfusions. This dedication to safe practices ensures that every donation has the potential to save lives without compromising patient well-being.
Remember: your decision to donate blood not only helps those in need but also contributes towards maintaining high standards of safety within healthcare systems worldwide!
Now is a great time to look into phlebotomy as a new career. You can get the hands on experience and help save lives with the American Red Cross. The American Red Cross has locations near you and all over the United States.
You can become a phlebotomist in as little as six weeks. You also have the option to take an online or in-person class with our school, Phlebotomy Career Training.
Our online students will receive a free phlebotomy practice kit or VSK (Virtual Simulation Kit) which you can practice. The practice arm is very life like and contains veins that feel like human veins.
This article was written by Nancy Lydia Kimmel PhD, RN, FNP-BC


Nancy L. Kimmel obtained her PhD in Environmental Engineering in 2002, then went on to teach Physics and Mechanical Engineering at Lawrence Technological University, Henry Ford College and Oakland University. She obtained her Associate in Nursing from Henry Ford College and then went on to earn her Master Degree as a Family Nurse Practitioner and became Board Certified working as a licensed FNP in the State of Michigan. She then went on to Medical School where she is now in her 3rd year, and is also in the process of obtaining her Doctorate in Nursing Practice through Chamberlin University. She has authored the NET Study Guide, as well a several books on subjects of Math, ECG/EKG and Phlebotomy. She holds a patent on an Air Filter through the U.S. Patent Office.

